1.If Statement
it is a conditional statement.. The if statement is used to execute the code, only when a condition is true.
if (condition)
{
statements
}
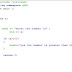
Example 1. checking if a number is greater than 100
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int a;
cout << "enter the number \n" ;
cin >> a;
if (a>100)
{
cout<<"yes the number is greater than 100" ;
}
return 0;
}
similarly you can use
>= greater than or equal to
<= less than or equal to
equal to==
!= not equal to
Example 2. checking the greater number out of two
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int a;
int b;
cout<< "enter a number a\n" ;
cin>> a;
cout << "enter another number b\n" ;
cin>> b;
if (a>b)
{
cout<< "a is greater than b";
}
if (b>a)
{
cout<< "b is greater than a" ;
}
if (b==a)
{
cout<< "both are equal" ;
}
return 0;
}
2.If-Else Statement
if (condition)
{ statements}
else
{statements}
Example 1. fail/pass in an exam
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int marks;
cout << "enter your marks\n" ;
cin>> marks;
if (marks<33)
{
cout<< "failed";
}
else
{
cout<<"passed\n" << "congratulations";
}
return 0;
}
3.Nested If Statements
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int age;
cout <<"enter ur age" ;
cin>> age;
if( age>14)
{
if (age>=18)
{
cout<< "adult" ;
}
else
{
cout <<"teenager";
}
}
return0;
}
the above program wont give any output for age less than 14...
for that, you will need another else statement.
4.Nested If-Else Statements
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int age;
cout <<"enter ur age \n" ;
cin>> age;
if( age>=13)
{
if (age>=18)
{
cout<< "adult" ;
}
else
{
cout <<"teenager";
}
}
else { cout<<"you are a kid";}
return 0;
}
it is a conditional statement.. The if statement is used to execute the code, only when a condition is true.
if (condition)
{
statements
}
Example 1. checking if a number is greater than 100
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int a;
cout << "enter the number \n" ;
cin >> a;
if (a>100)
{
cout<<"yes the number is greater than 100" ;
}
return 0;
}
similarly you can use
>= greater than or equal to
<= less than or equal to
equal to==
!= not equal to
Example 2. checking the greater number out of two
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int a;
int b;
cout<< "enter a number a\n" ;
cin>> a;
cout << "enter another number b\n" ;
cin>> b;
if (a>b)
{
cout<< "a is greater than b";
}
if (b>a)
{
cout<< "b is greater than a" ;
}
if (b==a)
{
cout<< "both are equal" ;
}
return 0;
}
2.If-Else Statement
if (condition)
{ statements}
else
{statements}
Example 1. fail/pass in an exam
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int marks;
cout << "enter your marks\n" ;
cin>> marks;
if (marks<33)
{
cout<< "failed";
}
else
{
cout<<"passed\n" << "congratulations";
}
return 0;
}
3.Nested If Statements
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int age;
cout <<"enter ur age" ;
cin>> age;
if( age>14)
{
if (age>=18)
{
cout<< "adult" ;
}
else
{
cout <<"teenager";
}
}
return0;
}
the above program wont give any output for age less than 14...
for that, you will need another else statement.
4.Nested If-Else Statements
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int age;
cout <<"enter ur age \n" ;
cin>> age;
if( age>=13)
{
if (age>=18)
{
cout<< "adult" ;
}
else
{
cout <<"teenager";
}
}
else { cout<<"you are a kid";}
return 0;
}
In the next blog,you will get to learn about loops.














No comments:
Post a Comment